Generate structural components
The new command is engineered to generate a structural component (ontology, concept, or properties) for Openfabric
development or integration purposes.
Usage: new [-hV] [COMMAND]
Create structural element (ontology, concept or properties).
Commands:
ontology Create ontology.
concept Create concept.
property Create properties connected to concept.
Create ontology
The ofc new ontology command enables you to generate a new ontology, which is essentially a namespace that encompasses
a collection of concepts.
Usage: ofc new ontology [-hV] [-d=<location>] [-s=<schema>] <name> <author>
Create ontology.
<name> ontology name
<author> author name
-d, --dest=<location> store location (format <TYPE:resource>)
-h, --help Show this help message and exit.
-s, --schema=<schema> ontology schema (format <ID>)
-V, --version Print version information and exit.
Below is an example of how to create an ontology called Universe authored by Andrei stored on local
system in the ./face-app directory:
$ ofc new ontology Universe Andrei --dest=DIR:./face-app
Create concepts
The new concept command enables you to generate one or several concepts.
Usage: ofc new concept [-hV] [-d=<location>] [-s=<schema>] [<name>[,
<name>...]...]
Create concept.
[<name>[,<name>...]...]
name of the concept(s) to generate
-d, --dest=<location> store location (format <TYPE:resource>)
-h, --help Show this help message and exit.
-s, --schema=<schema> ontology schema (format <ID>)
-V, --version Print version information and exit.
Below is an example of how to create the concepts face_input, face_position, and face_output stored on local
system in the ./face-app directory:
$ ofc new concept face_input,face_position,face_output --dest=DIR:./face-app
Be mindful of how the new concept command receives its inputs; face_input,face_position,face_output should be entered
as comma-separated concept names.
Populate concepts with properties
The new property command enables you to generate one or several properties for a given concept.
Usage: ofc new property [-hV] [-d=<location>] [-s=<schema>] <name> [<property>[,
<property>...]...]
Create properties connected to concept.
<name> target concept name
[<property>[,<property>...]...]
properties list
-d, --dest=<location> store location (format <TYPE:resource>)
-h, --help Show this help message and exit.
-s, --schema=<schema> ontology schema (format <ID>)
-V, --version Print version information and exit.
Now that we have created the concepts we are going to populate them with the required properties.
So in our example the face input will be an image from a webcam, this means we are going to add a property called
image of type camera
$ ofc new property face_input image:camera --dest=DIR:./face-app
The face output will contain a list of faces and their corresponding positions, for this we are going to define the face position properties as follows:
$ ofc new property face_position name:string,x:integer,y:integer,width:integer,height:integer --dest=DIR:./face-app
$ ofc new property face_output faces:face_position:1/n --dest=DIR:./face-app
Please note the 1/n parameter representing the
cardinality argument. It basically specifies that faces contains an array of face_position concepts,
having a minimum of 1 element.
Another important aspect to notice is the comma-separated list of properties following the pattern name:type where the type can be a primitive type (please find below the table of supported data types) or a reference type pointing to another existing concept as the face_position property in our example.
| Primitive | Description |
|---|---|
| string | A string data type used for input and display of short text values. |
| boolean | A logical data type used for input and display of Boolean (true/false) values. |
| short | A logical data type used for input and display of Boolean (true/false) values. |
| integer | A whole number data type used for input and display of integer values. |
| float | A numerical data type used for input and display of floating-point values. |
| double | A numerical data type used for input and display of double-precision floating-point values. |
| bigdecimal | A numerical data type used for input and display of high-precision decimal values. |
| biginteger | A numerical data type used for input and display of arbitrarily large integer values. |
| date | A data type used for input and display of date values. |
| time | A data type used for input and display of time values. |
| timestamp | A data type used for input and display of timestamp values. |
| datetime | A data type used to represent a specific date and time values. |
| text | The text primitive is employed to showcase extended passages of text, facilitating the presentation and editing of multiline content within your application. |
| dropdown | The dropdown primitive is designed to render dropdown menus, offering a compact and interactive way to present selectable options within your application. |
| camera | The camera primitive utilizes a webcam feed as the image source, enabling real-time capture and processing of visual data from the connected device. |
| recording | The recording primitive utilizes a webcam feed as the video source, enabling real-time video capturing from the connected device. |
| microphone | The microphone primitive leverages the output from your connected microphone to produce audio, facilitating real-time capture and processing of acoustic data. |
| blob | The blob primitive creates an upload component, enabling users to upload various file types, such as images, audio, video, and other required files, for seamless integration with your app. |
| webgl | The webgl primitive is employed to render 3D models within your application, enabling interactive and immersive visualization of complex geometries and graphics using web-based technologies. |
UI Layout
- The data types String, Integer, Float, Double, BigDecimal, and BigInteger will be showcased as input fields with corresponding data type validation to ensure that the entered values are of the correct data type.
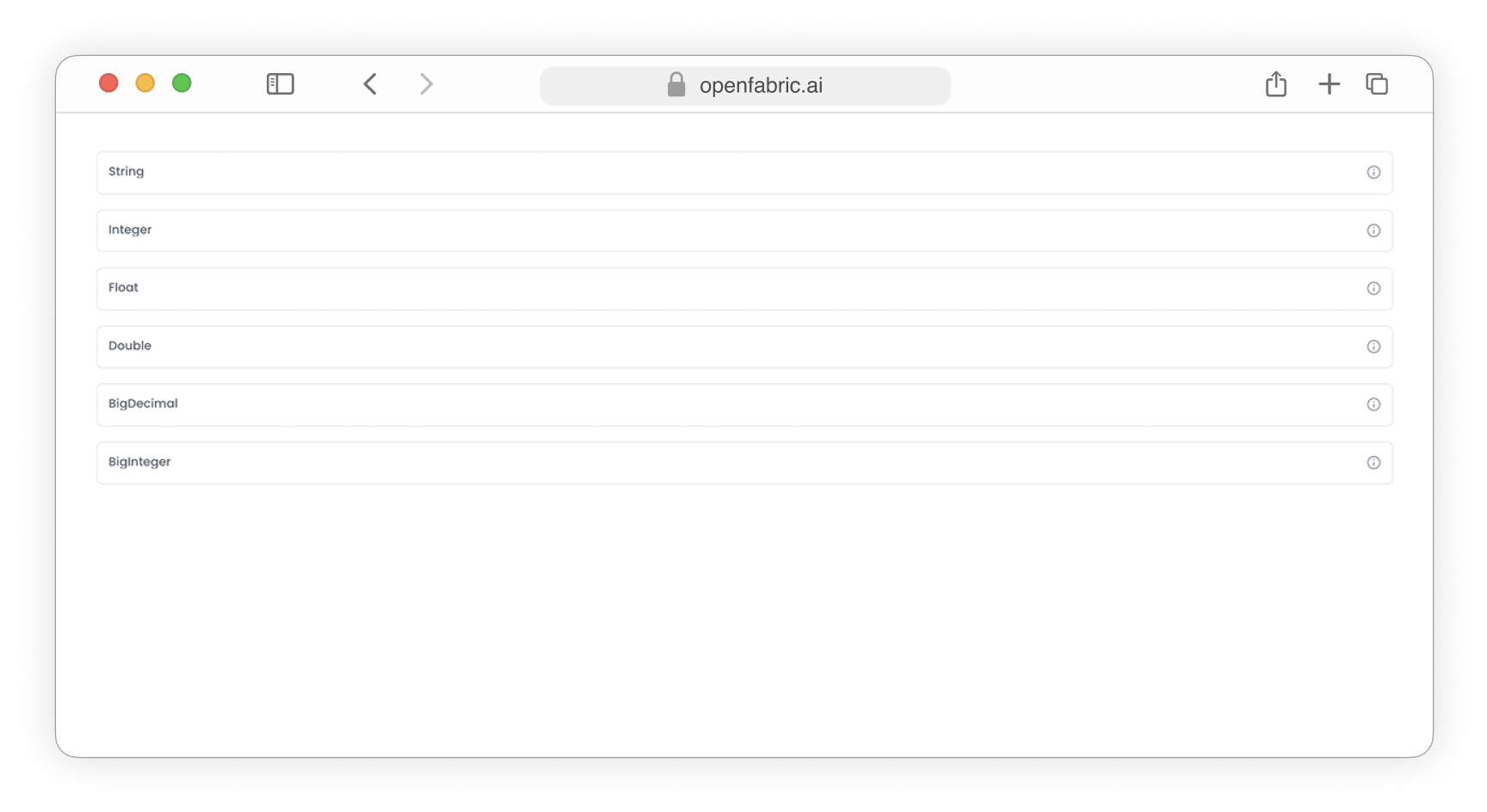
Fig. 1: Text input fields
-
The data type Text will be presented as a textarea input field
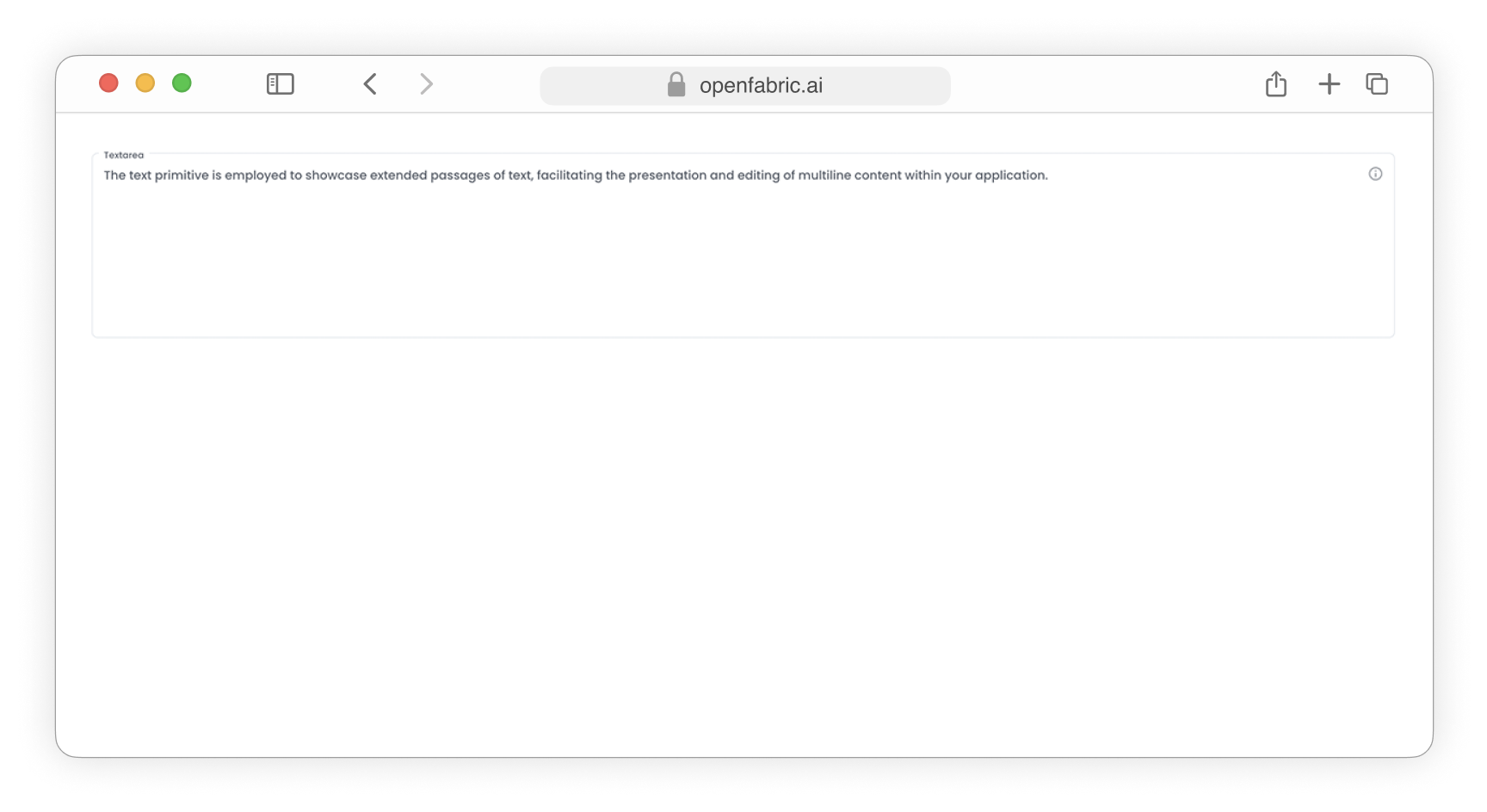
Fig. 2: Textarea input field
-
The data types Short and Boolean will be showcased as dropdown input fields, enabling users to select and modify the desired value from a list of options.
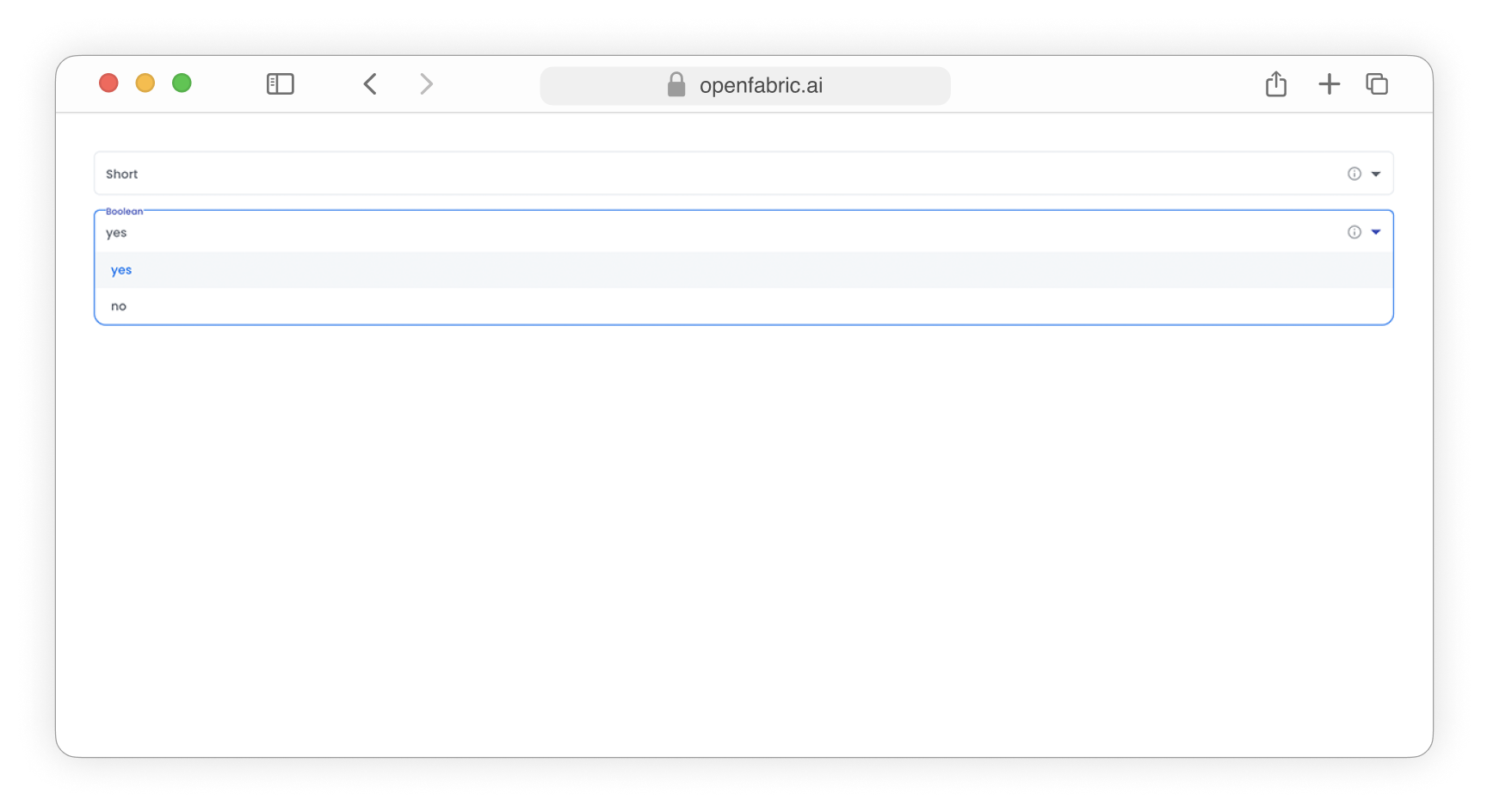
Fig. 3: Dropdown input fields
- The data types Date, Time, Timestamp, and Datetime will be presented as calendar input fields, enabling users to select and modify the desired date or time value with ease and accuracy.
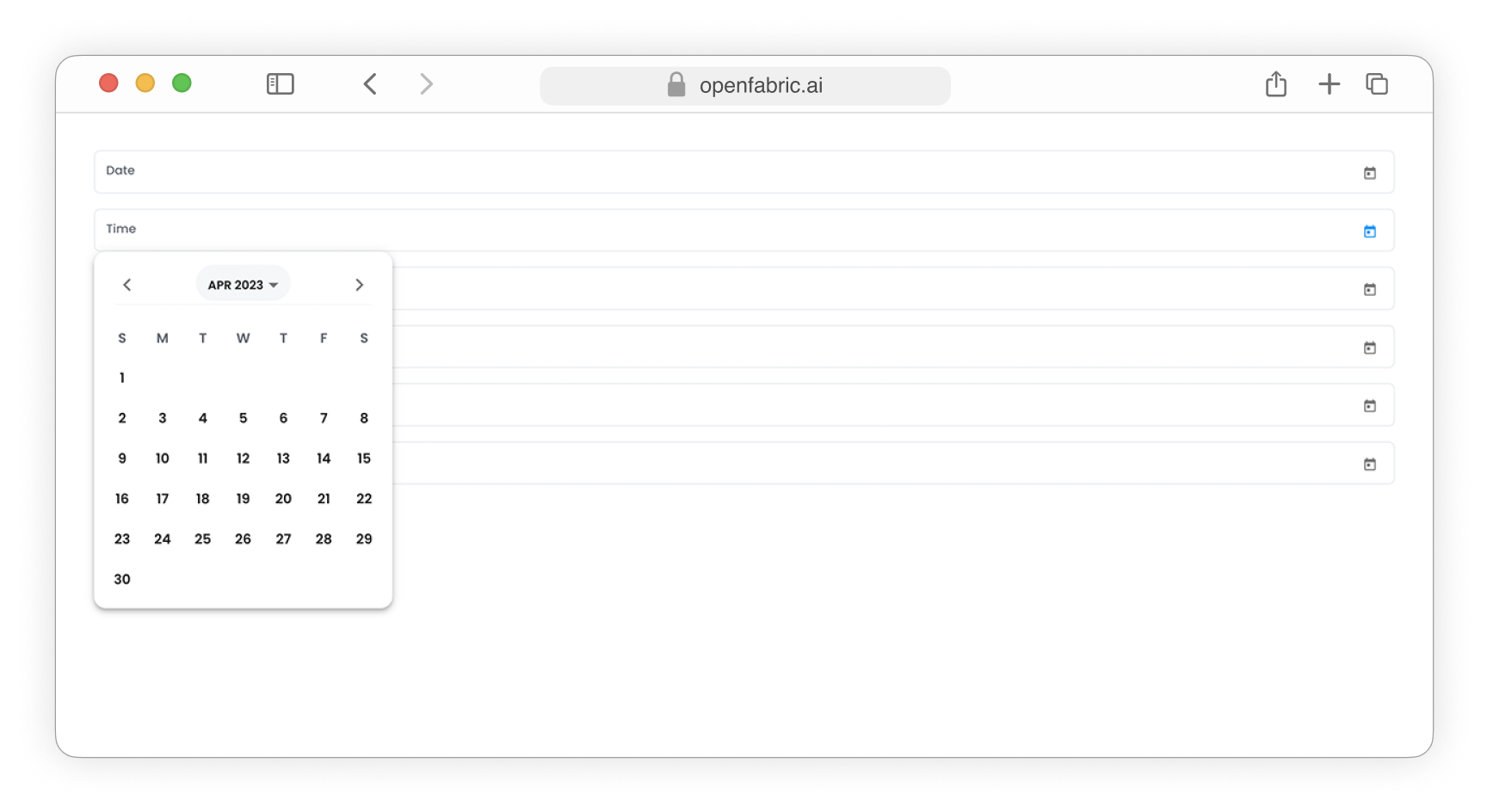
Fig. 4: Date input fields
- The Camera data type will be showcased as a webcam feed, allowing users to capture and display live camera images from their computer's camera.
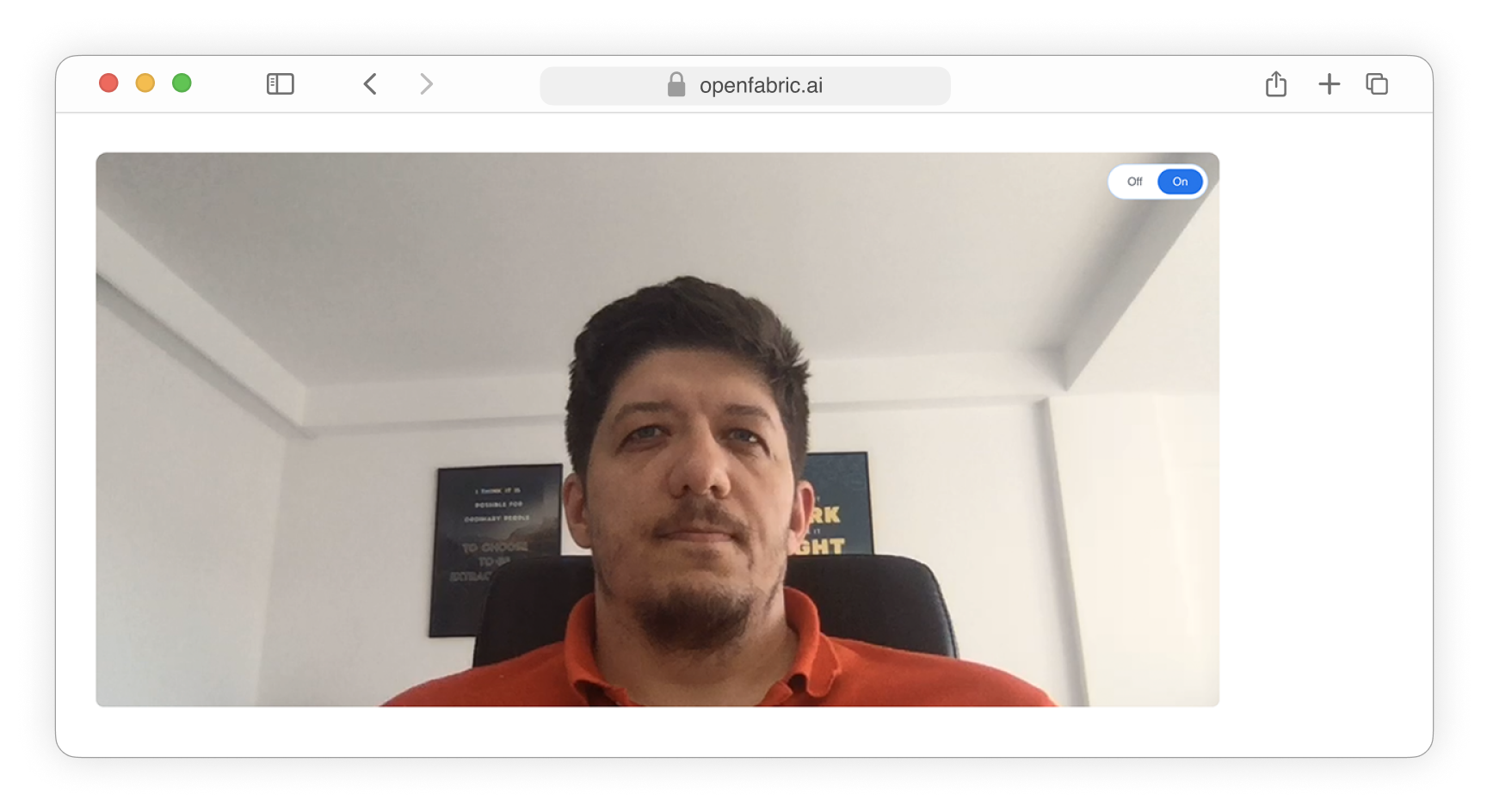
Fig. 5: Camera field
- The Recording data type will be showcased as a webcam feed, allowing users to capture and display live video footage.

Fig. 6: Recording field
-
The Blob data type will be presented as an upload input field, allowing users to select and upload files of various types, such as images, audio, video, archives, and other data files.
-
Upload videos
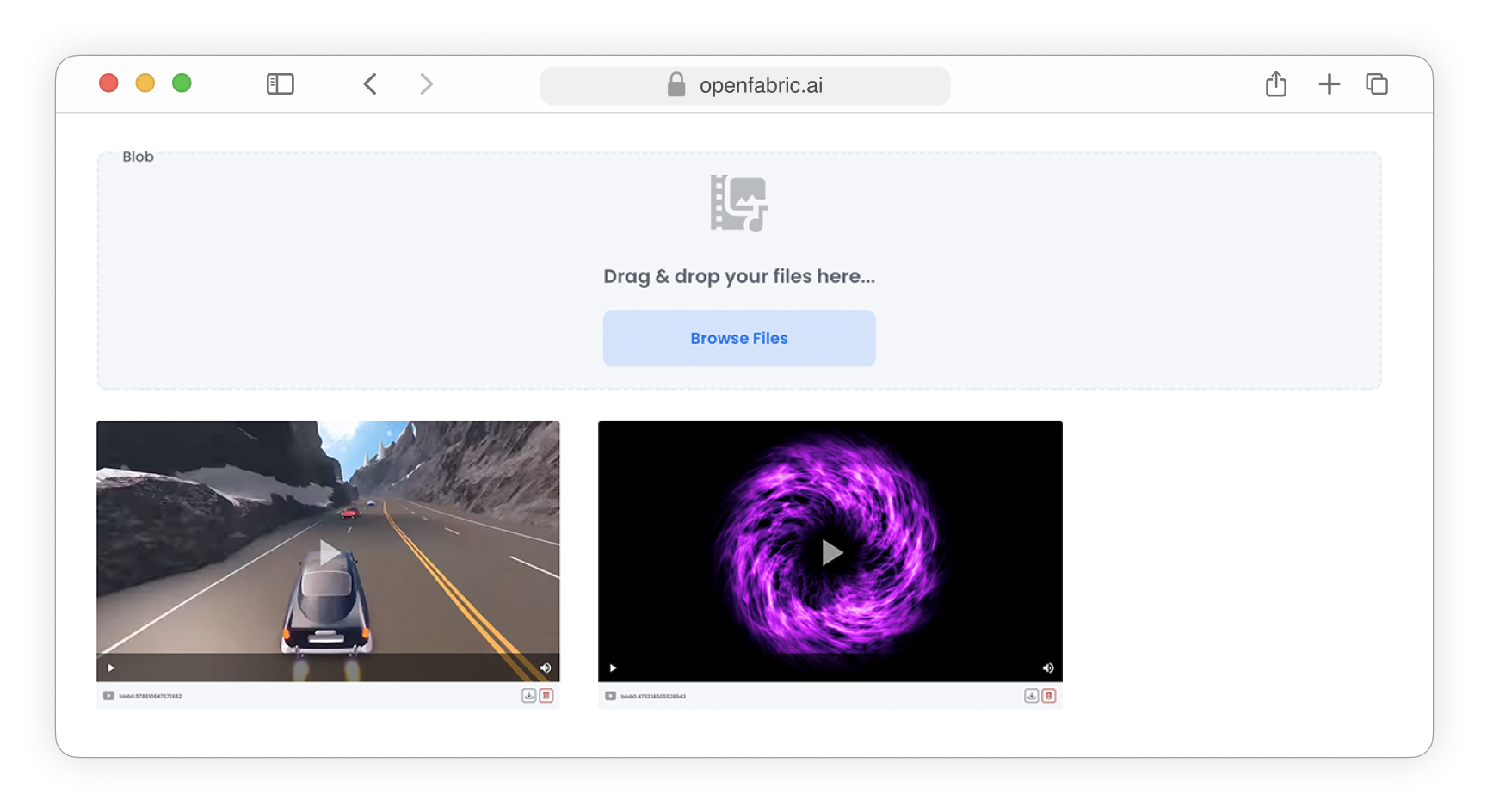
Fig. 7: Upload video
-
Upload images
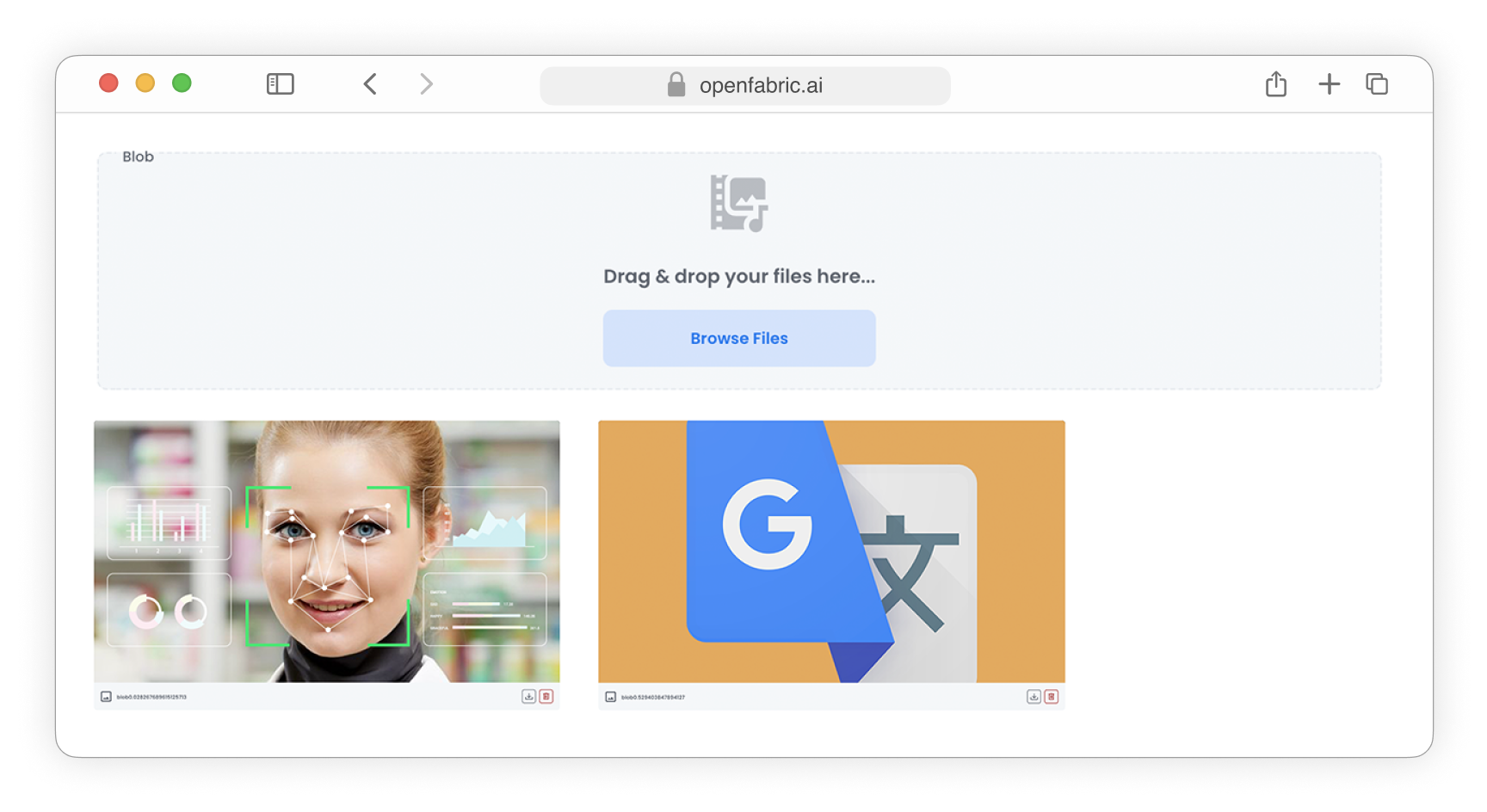
Fig. 8: Upload images
-
Upload archives
Fig. 9: Upload archives
-
Upload audio files
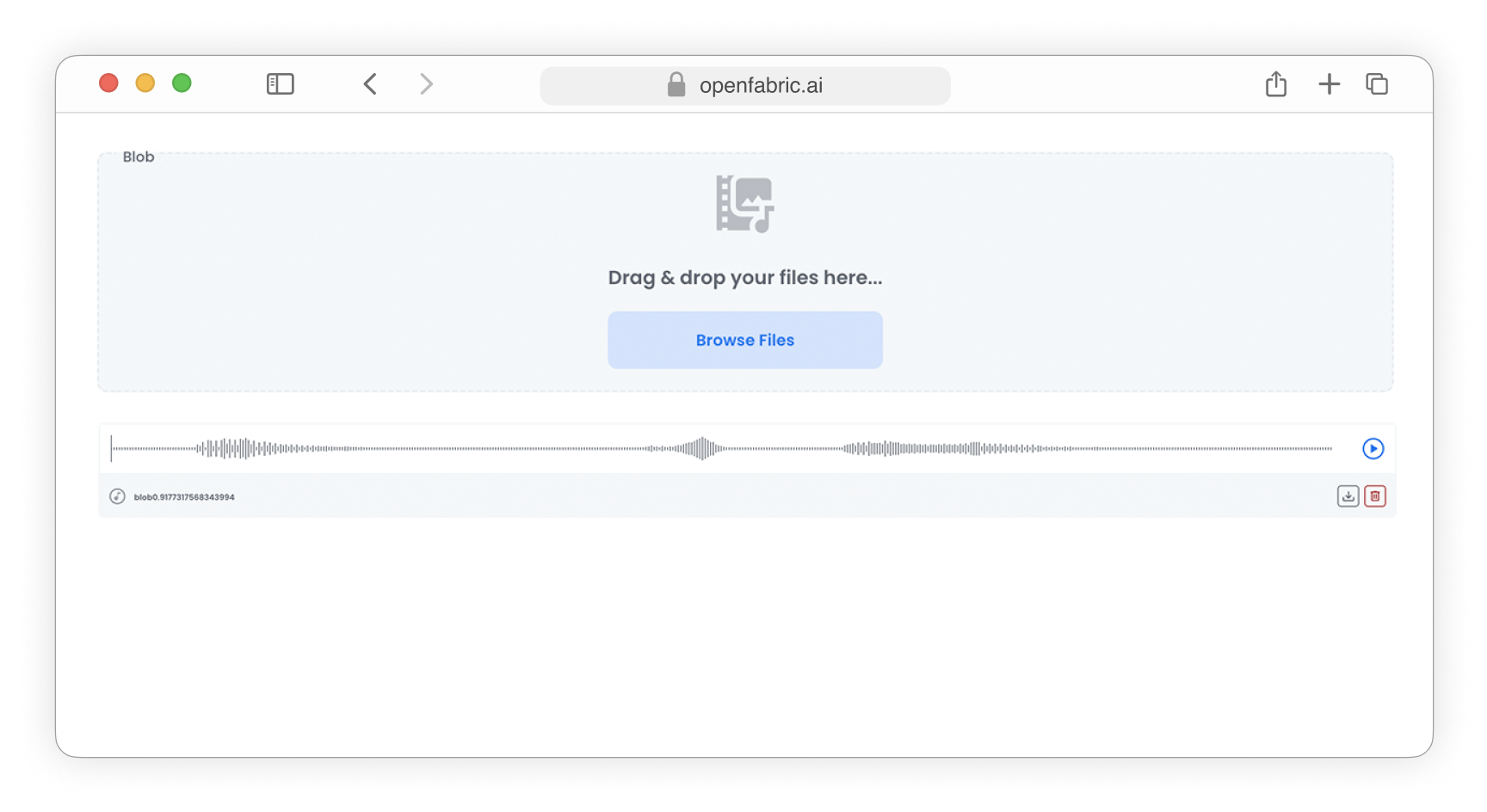
Fig. 10: Upload audio
-
The Microphone data type introduces a custom field specifically designed for capturing audio input directly from a microphone. This feature enables users to seamlessly record audio clips or voice messages within the application, providing a more interactive and dynamic user experience.
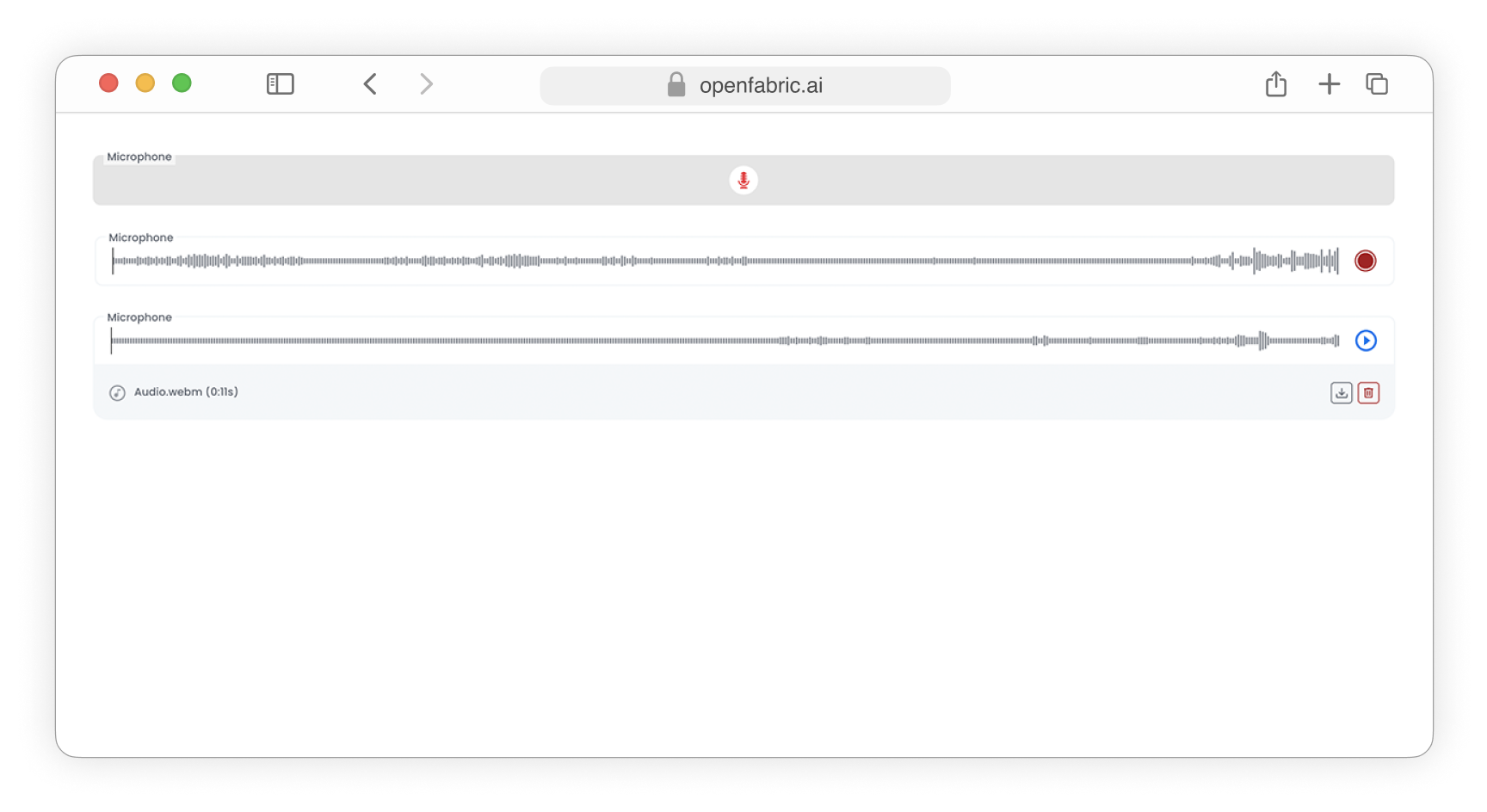
Fig. 11: Microphone field
- The Webgl primitive is employed to render 3D models within your application, enabling interactive and immersive visualization of complex geometries and graphics using web-based technologies.
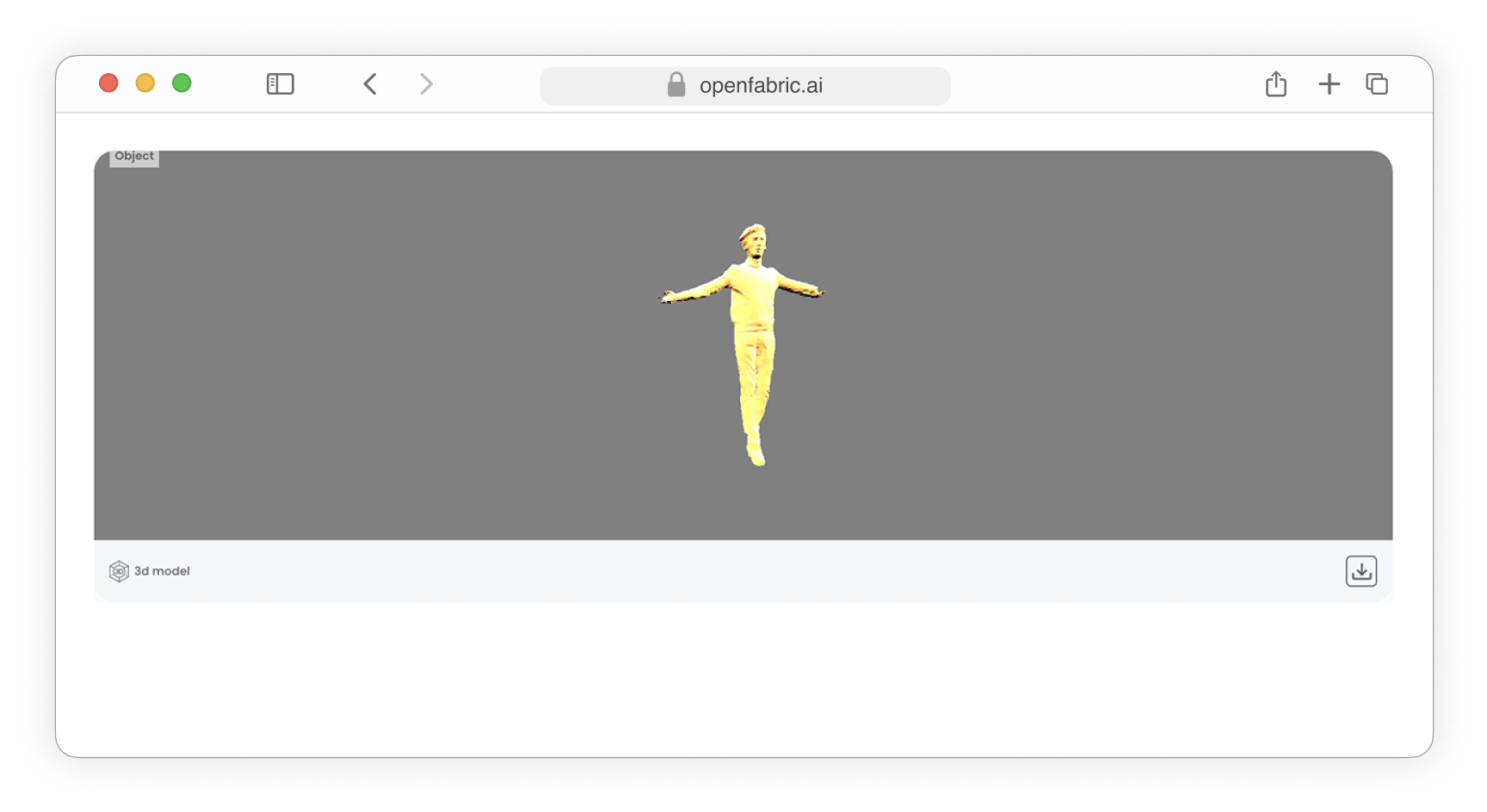
Fig. 12: Webgl field
